Introduction
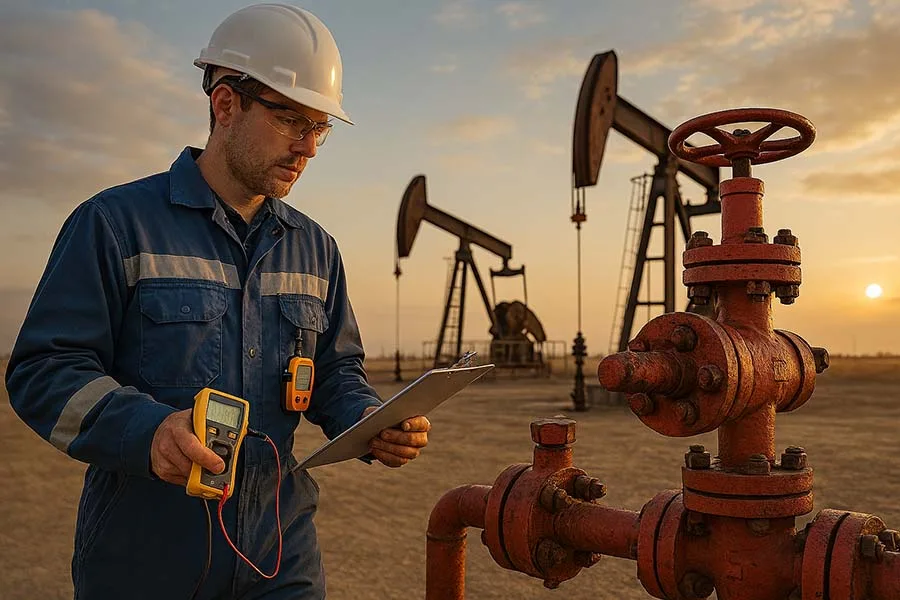
In the oil and gas industry, one small crack in a pipeline or a faulty weld can cost millions – or worse, put lives at risk. That’s why inspection and testing tools are at the heart of safe and reliable operations. From drilling rigs to refineries, every piece of equipment must be tested, monitored, and certified to withstand extreme conditions.
In this article, we’ll explore the most important inspection and testing tools used in oil and gas, how they work, and why they’re critical for both safety and efficiency.
Why Inspection and Testing Matter
Oil and gas operations face some of the harshest conditions on Earth – high pressures, corrosive materials, extreme temperatures, and remote locations. Inspection and testing tools ensure:
- Safety – Detecting cracks, leaks, or weaknesses before they cause disasters.
- Compliance – Meeting strict industry standards and government regulations.
- Efficiency – Preventing costly downtime by catching problems early.
- Longevity – Extending the life of pipelines, valves, and heavy machinery.
Key Inspection and Testing Tools
1. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Tools
NDT allows engineers to test materials without damaging them. Common NDT methods include:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT) – Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws.
- Radiographic Testing (RT) – X-rays or gamma rays reveal hidden cracks in welds.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) – Identifies surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
- Dye Penetrant Testing (PT) – Highlights surface cracks using a visible dye.
2. Pipeline Inspection Gauges (PIGs)
Known as “pipeline pigs”, these devices travel through pipelines to inspect internal conditions. Smart PIGs can detect corrosion, cracks, and even measure wall thickness using sensors and magnets.
3. Pressure Testing Equipment
Pipelines, tanks, and valves are subjected to hydrostatic and pneumatic pressure tests to verify their integrity under extreme conditions.
4. Leak Detection Tools
Advanced gas detectors, acoustic sensors, and infrared cameras can identify leaks before they become catastrophic.
5. Vibration and Acoustic Testing
Monitoring vibrations in pumps, compressors, and turbines helps predict mechanical failures before they occur.
6. Drone and Robotics Inspection
Modern refineries and offshore rigs use drones for flare stack inspections and ROVs for subsea pipelines – reducing human risk and increasing accuracy.
Digital Advancements in Testing
The integration of digital technologies has revolutionized oil and gas inspection:
- IoT sensors provide real-time condition monitoring.
- AI algorithms analyze inspection data for faster decision-making.
- Digital twins simulate asset performance under various conditions.
- Cloud-based reporting allows instant sharing of inspection results across global teams.
Challenges in Inspection and Testing
Despite technological advances, some challenges remain:
- Harsh environments make inspections difficult and dangerous.
- Cost of advanced tools can be a barrier for smaller operators.
- Data overload from digital tools requires skilled interpretation.
- Human expertise is still needed for complex evaluations.
Future Outlook
Inspection and testing will continue moving toward automation and predictive analytics. Expect to see:
- More AI-driven inspections for faster, more accurate fault detection.
- Increased use of autonomous drones and robots in hazardous areas.
- Sustainability-focused testing to reduce emissions and energy use during inspections.
Funny Fact
The nickname “pipeline pig” comes from the squealing noise early inspection tools made as they traveled through pipelines – engineers really heard them “oink” their way along!
Lesser-Known Fact
The very first pipeline inspection tool was used in the 1960s and was no smarter than a steel brush. Today’s PIGs, in contrast, are packed with electronics and can map a pipeline with GPS-level precision.
Further Reading
- Industrial Tools in the Energy and Oil Industry
- Drilling and Extraction Tools in the Oil Industry: Complete Guide 2025
- Maintenance Tools for Oil Refineries: Complete Guide to Essential Equipment
- Pipeline Construction and Repair Tools | Essential Guide for Oil & Energy
- Safety Tools and Equipment in the Energy Sector
- Automation and Digital Tools in Oil & Gas
- Heavy Machinery in Oil and Energy Production
- Inspection and Testing Tools in Oil & Gas
- Tool Innovations Shaping the Future of Oil and Energy
Conclusion
Inspection and testing tools are the silent guardians of the oil and gas industry. They prevent accidents, ensure compliance, and extend the life of critical infrastructure. With the rise of AI and robotics, inspections are becoming faster, safer, and more reliable than ever.
What do you think – will inspection robots eventually replace human inspectors entirely, or will people always play a key role in final evaluations? Share your opinion in the comments!