Introduction: Why Refinery Maintenance Tools Matter
Oil refineries are some of the most complex industrial sites on the planet. They operate 24/7, processing thousands of barrels of crude oil daily, and every piece of equipment is under constant stress. Without the right maintenance tools, refinery operations would grind to a halt – or worse, face catastrophic failures.
In this guide, we’ll explore the essential maintenance tools for oil refineries, their technical specifications, pros and cons, and the innovations shaping the future of refinery maintenance.
Key Categories of Refinery Maintenance Tools
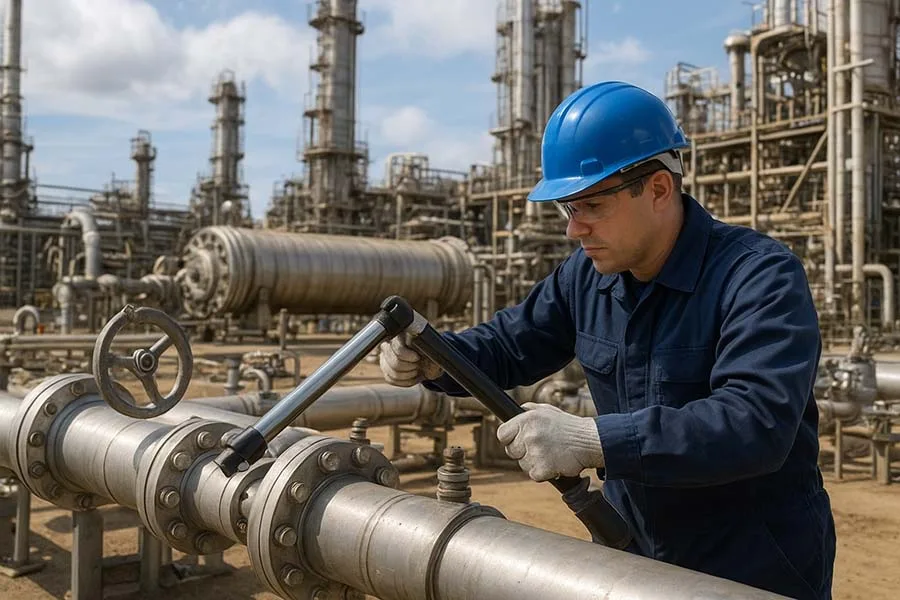
1. Torque Wrenches and Bolting Tools
- Purpose: Ensure precise tightening of flanges, heat exchangers, and pressure vessels.
- Types: Hydraulic torque wrenches, pneumatic torque tools, and digital torque devices.
- Specs That Matter:
- Torque range up to 20,000 Nm.
- Accuracy ±3% for critical joints.
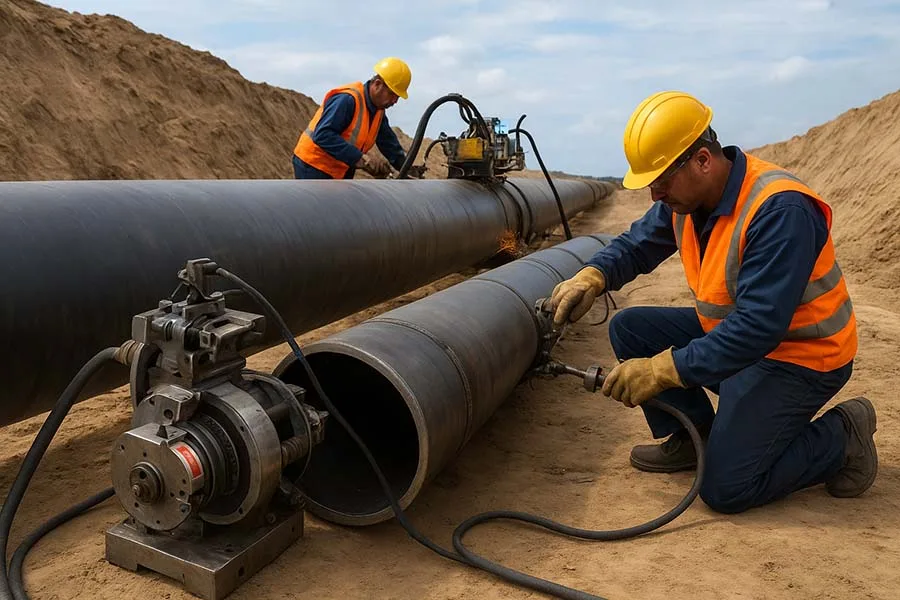
2. Pumps and Valve Maintenance Tools
- Examples: Portable pump skids, valve grinding machines, automated valve testers.
- Function: Maintain flow control in refining units such as catalytic crackers and distillation towers.
- Challenge: Valves operate under high temperatures and corrosive conditions, requiring constant upkeep.
3. Heat Exchanger Cleaning Tools
- Techniques:
- Hydroblasting (ultra-high pressure water jets up to 40,000 psi).
- Chemical cleaning systems.
- Tube bundle pullers.
- Goal: Remove fouling and maintain energy efficiency.
4. Inspection and Monitoring Devices
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Ultrasonic flaw detectors, radiographic testing, magnetic particle inspection.
- New Tech: Drones and robotic crawlers for confined spaces.
- Specs:
- Ultrasonic probes detecting cracks smaller than 0.1 mm.
- ATEX-rated drones for explosive atmospheres.
5. Fire and Gas Safety Systems
- Examples: Gas detectors, flame arresters, emergency shutdown systems.
- Specs: Detection thresholds down to parts per million (ppm).
- Note: These aren’t just safety devices — they’re legally required in most refineries.
Technical Specifications That Matter
- Torque Tool Accuracy: ±3% on critical joints.
- Pump Pressure for Hydroblasting: Up to 40,000 psi.
- Inspection Camera Resolution: 4K visual inspection cameras with thermal overlays.
- Valve Test Pressure: Up to 10,000 psi to simulate operating conditions.
Pros and Cons of Refinery Maintenance Tools
Advantages:
- Improve safety and reduce risk of leaks or explosions.
- Extend lifespan of refinery equipment.
- Increase energy efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Allow predictive maintenance using IoT and sensors.
Disadvantages:
- High costs of advanced inspection tools and robotic systems.
- Require highly skilled operators and certifications.
- Downtime during maintenance still impacts production.
- Tools degrade quickly in corrosive refinery environments.
Interesting Facts
Funny Fact: Refinery workers often say torque wrenches are “refinery babysitters” — without them, every bolt and flange would throw a tantrum.
Lesser-Known Fact: Many modern refineries use acoustic emission testing, a method where tiny sound waves from stressed metal are detected to identify cracks before they become visible.
Maintenance Tools for Refineries FAQ
Conclusion: Tools That Keep Refineries Running
Refinery maintenance tools are the unsung heroes of the oil and gas sector. From torque wrenches to drones, each tool contributes to keeping refineries safe, efficient, and operational. As refineries adopt more automation and predictive systems, these tools will only become more advanced and indispensable.
Further Reading
- Industrial Tools in the Energy and Oil Industry
- Drilling and Extraction Tools in the Oil Industry: Complete Guide 2025
- Maintenance Tools for Oil Refineries: Complete Guide to Essential Equipment
- Pipeline Construction and Repair Tools | Essential Guide for Oil & Energy
- Safety Tools and Equipment in the Energy Sector
- Automation and Digital Tools in Oil & Gas
- Heavy Machinery in Oil and Energy Production
- Inspection and Testing Tools in Oil & Gas
- Tool Innovations Shaping the Future of Oil and Energy
- Best Smart Tightening Tools for Industrial Assembly (2025 Guide)
💬 Your Turn:
Have you ever seen or worked with refinery maintenance tools in action? Share your experiences or thoughts in the comments below — and don’t forget to share this article if you found it useful!