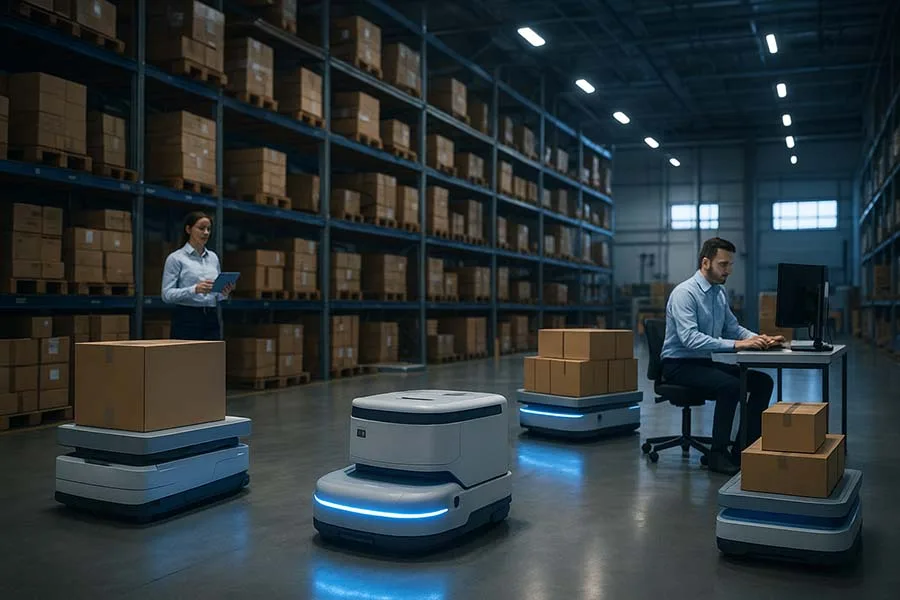
In warehouses, distribution centers, and factories worldwide, a quiet revolution is underway. It’s not loud, flashy, or humanoid—it’s silent, efficient, and on wheels. Mobile robots and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have become the backbone of logistics, moving goods, feeding production lines, and keeping global supply chains running with astonishing efficiency.
These silent workers rarely get the spotlight, but they are reshaping logistics as profoundly as container shipping did decades ago. Let’s explore their reality: benefits, challenges, technical features, and where they’re heading next.
What Are Mobile Robots and AGVs?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are wheeled robots that transport materials across warehouses or factory floors, usually following fixed paths (magnetic strips, QR codes, or wires).
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) represent the next step—using advanced sensors, vision, and AI to navigate dynamically without fixed infrastructure.
In short:
- AGVs: Reliable, infrastructure-based navigation.
- AMRs: Flexible, intelligent, map-based navigation.
Both are central to modern logistics and often coexist on the same shop floor.
Why Mobile Robotics Matters in Logistics
The global e-commerce boom and “just-in-time” supply chains have pushed warehouses to operate faster, safer, and smarter. Mobile robots help achieve this by:
- Boosting Productivity: Robots reduce walking distances for humans, shaving hours off daily workflows.
- Reducing Costs: An AGV fleet can replace forklifts and manual transport, saving on labor and accident costs.
- Enhancing Safety: Robots don’t get tired or distracted. Fewer accidents and damaged goods.
- Scalability: Fleets of AGVs can be scaled up or down depending on seasonal demand.
📈 Industry Fact: According to Interact Analysis, the global mobile robot market is projected to reach $18 billion by 2027, with warehouses leading adoption.
💡 Funny Fact: Some warehouses paint “robot lanes” on the floor—like highways—so humans don’t accidentally cut off traffic. Yes, even robots need their own traffic rules.
Challenges and Reality Check
While they’re efficient, mobile robots and AGVs bring their own challenges:
- High Upfront Investment: Depending on size and complexity, a single AGV can cost between $50,000 and $150,000.
- Infrastructure Needs (AGVs): Traditional AGVs require tracks, wires, or beacons, which limit flexibility.
- Integration with WMS/ERP: To be effective, robots must “talk” to warehouse systems in real-time.
- Downtime Risks: If one robot in a tightly choreographed system fails, it can create bottlenecks.
- Human Adaptation: Workers must adjust to new workflows and safety protocols.
Reality check: Mobile robots are not “plug-and-play” miracles—they need planning, IT integration, and cultural acceptance.
Human vs. Mobile Robot Strengths
| Feature | Human Workers | Mobile Robots / AGVs |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Extremely adaptable, can improvise | Limited to programmed tasks |
| Endurance | Fatigue over long shifts | Continuous operation, 24/7 |
| Navigation | Intuitive, can handle obstacles easily | Sensors + AI, but struggle in chaos |
| Safety Awareness | Instinctive, context-driven | Lidar, vision, collision sensors |
| Cost Over Time | Ongoing wages and training | High upfront, lower long-term cost |
Conclusion: Humans and robots complement each other. Robots move goods tirelessly; humans handle problem-solving and exceptions.
Key Technical Features of Mobile Robots and AGVs
Mobile robots come with cutting-edge technology that enables silent but powerful performance:
- Navigation Systems: Magnetic tape, QR markers, SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping).
- Safety Sensors: Lidar, ultrasonic sensors, 3D vision cameras.
- Fleet Management Software: Optimizes routes, prevents collisions, and schedules tasks.
- Battery Tech: Lithium-ion batteries with auto-docking charging stations.
- Payload Ranges: From 100 kg for small robots to over 5,000 kg for heavy-duty AGVs.
Example Mobile Robot Specifications
| Model | Payload Capacity | Navigation Type | Speed | Application |
| MiR250 (Mobile Industrial Robots) | 250 kg | SLAM + laser | 2 m/s | Warehouse transport, material supply |
| KUKA KMP 1500 | 1500 kg | Laser + SLAM | 1.7 m/s | Automotive, heavy loads |
| Toyota Autopilot AGV | 500 kg | Magnetic tape | 1.5 m/s | Pallet transport |
Real-World Applications
- Amazon Fulfillment Centers: Over 500,000 mobile robots transport shelves and packages, dramatically cutting order fulfillment times.
- Automotive Manufacturing: AGVs deliver components just-in-time to assembly lines at companies like Toyota and BMW.
- Healthcare Logistics: Hospitals use small AMRs to deliver linens, food, and medicines.
💡 Lesser-Known Fact: Some AGVs are designed for extreme environments, like underground mining, where they haul ore through tunnels without human drivers.
Future Outlook: Towards Autonomous Logistics
The future of logistics will see hybrid fleets—AGVs for predictable heavy loads, AMRs for dynamic environments. AI and machine vision will push robots toward full autonomy.
Predictions:
- Full Warehouse Automation: By 2035, many warehouses may run entirely on fleets of robots with minimal human supervision.
- Human Role Shift: Workers will transition into fleet managers, maintenance specialists, and logistics analysts.
- Sustainability Gains: Robots optimize routes and reduce wasted energy, lowering the carbon footprint.
Mobile Robotics and AGVs FAQ
Read more about Robotics & Intelligent Automation in Industry
- Robotics & Intelligent Automation in Industry
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
- AI & Machine Vision: How Smart Robots See, Think, and Adapt
- Precision Engineering Meets Robotics
- The Economics of Robotics: Cost, ROI, and When to Automate
- Robotics Safety Standards Every Manufacturer Should Know
- Humans and Robots: The Reality of Shop Floor Collaboration
- Mobile Robotics and AGVs: The Silent Workforce of Logistics
- Robotics in Small and Medium Manufacturing
- The Future of Industrial Tools in a Robotic World
- Disruptive Trends: AI, 5G, and Digital Twins in Robotics
Conclusion
Mobile robots and AGVs may not make headlines like humanoid robots, but they are the silent workforce powering logistics. They move goods with precision, reliability, and speed—enabling the growth of e-commerce and modern manufacturing. As technology advances, expect them to become even more autonomous, sustainable, and indispensable.
👉 Would you welcome a robot colleague silently carrying pallets past you every day? Share your thoughts below!