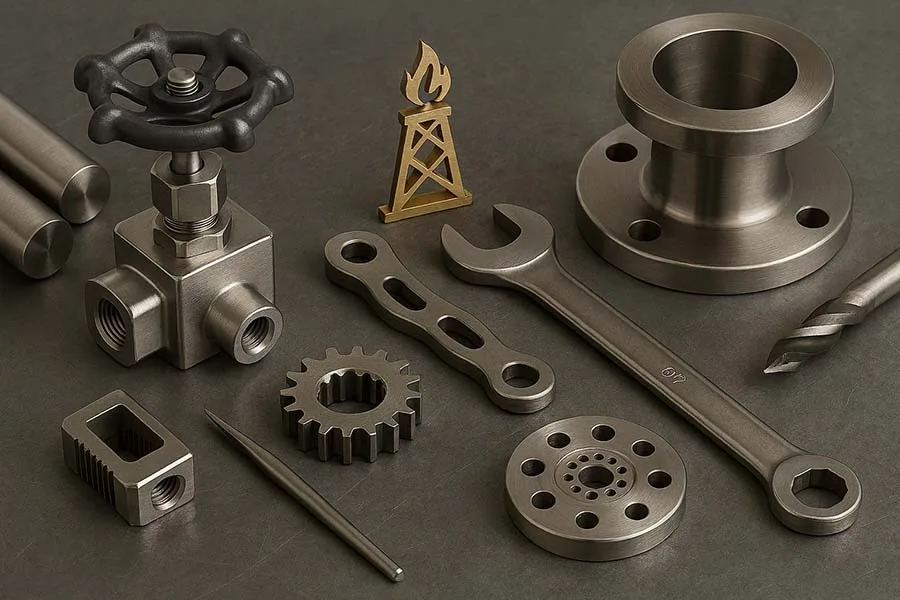
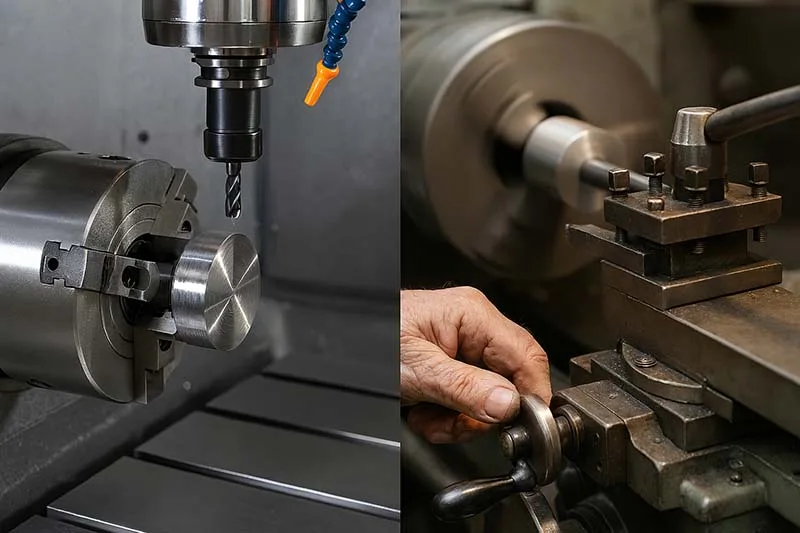
CNC machining plays a vital role in energy and oil equipment manufacturing, from turbines and pumps to valves and pipelines. High-precision machining ensures safety, efficiency, and reliability in an industry where component failure can be catastrophic.
In this article, we’ll explore how CNC is applied in energy and oil equipment production, the materials used, key machining processes, quality standards, emerging trends, and practical considerations for manufacturers.
Why CNC is Critical in Energy & Oil Equipment
Energy and oil equipment requires components with tight tolerances, high durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. CNC machining provides:
- High Precision: Critical for turbine blades, pump rotors, and valve components.
- Repeatability: Ensures identical performance across multiple units.
- Complex Geometries: Components often require intricate 3D shapes for fluid dynamics and mechanical efficiency.
- Durability: Machined parts meet rigorous standards for wear, heat, and pressure.
Fun Fact: Some offshore oil rig components are machined to tolerances within 0.01 mm, ensuring reliability in harsh environments.
Materials Used in Energy & Oil CNC Machining
The energy sector relies on metals and superalloys that can withstand extreme pressures, temperatures, and corrosion.
1. Metals
| Metal | Properties | Machinability | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, strong | Moderate | Valves, pumps, pipelines |
| Carbon Steel | High strength, durable | Excellent | Structural components, machinery |
| Nickel-based Superalloys | Heat-resistant, wear-resistant | Difficult | Turbine blades, gas turbine components |
| Titanium | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Challenging | Offshore equipment, subsea components |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Excellent | Auxiliary components, housings |
Practical Tip: Nickel-based superalloys and titanium are often used for turbine and high-stress components, while carbon and stainless steel are common for valves, pipelines, and structural elements.
2. Composites & Specialty Materials
| Material | Properties | Machinability | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber | Lightweight, strong | Challenging | Offshore equipment housings, structural reinforcements |
| Fiberglass | Durable, corrosion-resistant | Moderate | Insulation panels, protective covers |
| Ceramics | High heat resistance, wear-resistant | Difficult | High-temperature nozzles, seals |
Lesser-Known Fact: Some subsea components combine metal and composite layers to optimize corrosion resistance and reduce weight for offshore applications.
CNC Processes in Energy & Oil Equipment
Machining energy and oil components often involves multi-step CNC operations:
- Milling: Produces turbine blades, pump housings, and valve bodies.
- Turning: Creates shafts, rotors, and cylindrical pump components.
- Drilling & Boring: Ensures precise fluid flow channels, mounting holes, and pipeline fittings.
- Multi-Axis Machining: 4–5 axis machines allow complex geometries for turbine blades, impellers, and pump rotors.
Tip: High-speed CNC machining improves productivity while maintaining tight tolerances for critical energy components.
Quality Standards and Safety Requirements
Energy and oil components are subject to strict industrial standards:
- API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas equipment.
- ISO 9001 & ISO 14001 for quality and environmental management.
- Inspection Methods:
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) for dimensional accuracy
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) for cracks, corrosion, or defects
- Laser scanning for precise surface verification
Practical Tip: CNC machining supports traceability and documentation, essential for safety audits and regulatory compliance.
Emerging Trends in Energy & Oil CNC Manufacturing
- Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining CNC with additive processes for complex or custom components.
- Automation & Robotics: CNC integrated into robotic production for increased efficiency and safety.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Optimizing material usage and reducing waste for environmentally friendly production.
- Advanced Materials: Machining advanced alloys and composites for high-performance turbines and offshore equipment.
Fun Fact: Offshore oil equipment can operate in extreme temperatures and pressures, so CNC machining tolerances are often tighter than in standard industrial applications.
Choosing CNC Solutions for Energy & Oil Equipment
Key considerations when selecting CNC machines for energy and oil applications:
- Machine Type: Multi-axis machines for complex turbine blades and pump rotors.
- Tooling: Must withstand wear from machining tough metals and superalloys.
- Material Expertise: Understanding machining parameters for corrosion-resistant alloys, composites, and ceramics.
- Collaboration: Close coordination between design engineers, machinists, and quality teams ensures optimal performance.
CNC in Energy & Oil Equipment FAQ
Read more about CNC Materials & Applications
- CNC Materials & Applications
- CNC in Energy & Oil Equipment
- Materials Used in CNC Machining
- CNC in Aerospace Manufacturing: Precision, Materials, and Technology
- CNC in Automotive Production
- CNC in Medical Devices
Conclusion
CNC machining is a cornerstone of energy and oil equipment manufacturing, producing components that are high-precision, durable, and compliant with strict industry standards. By leveraging advanced materials, multi-axis machining, and emerging trends like hybrid manufacturing, the energy sector can achieve reliability and efficiency, whether onshore, offshore, or in renewable energy applications.