Introduction: Two Titans of Modern Manufacturing
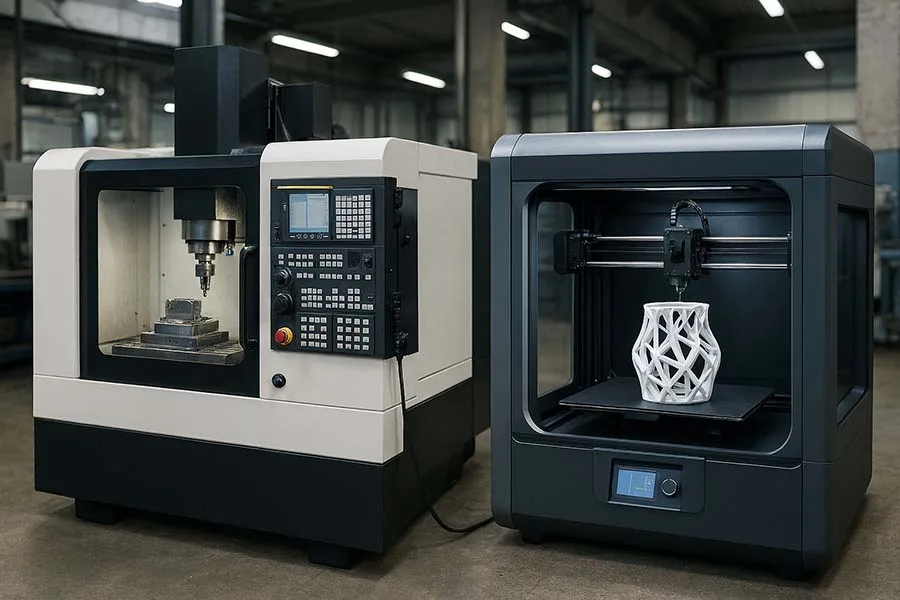
In the world of modern manufacturing, two technologies often steal the spotlight: CNC machining and 3D printing. While some see them as fierce competitors, others view them as complementary tools in a smart factory toolkit. The question is: should you pick sides, or can these two technologies work hand in hand to revolutionize production? Let’s break it down.
CNC Machining: Precision Meets Power
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has been a cornerstone of manufacturing for decades. Its strengths include:
- High precision and repeatability: Ideal for tight-tolerance parts.
- Material versatility: From metals to plastics and composites.
- Strong and durable output: Parts are often ready for demanding mechanical use without post-processing.
Lesser-known fact: Some CNC machines can handle tolerances as small as a few microns, which is finer than the width of a human hair!
Funny fact: CNC machines can run 24/7 without complaint—though they won’t bring you coffee.
3D Printing: The Rise of Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer from a digital model. Its advantages are:
- Design freedom: Complex geometries that are impossible with traditional machining.
- Rapid prototyping: Quickly turn concepts into physical models.
- Material innovation: From biodegradable plastics to high-performance metal powders.
Lesser-known fact: Some aerospace components printed in metal can be lighter and stronger than traditionally machined equivalents.
Funny fact: 3D printers are the only machines where failed prints look like modern art projects!
CNC vs 3D Printing: Strengths in Comparison
| Feature | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Extremely high | Medium to high (depends on tech) |
| Material Options | Metals, plastics, composites | Plastics, resins, metals, ceramics |
| Production Speed | Fast for mass production | Slower for high-volume parts |
| Design Complexity | Limited by tooling | Almost unlimited |
| Post-processing | Often minimal | Usually required (supports, finishing) |
| Cost Efficiency | Efficient for large batches | Efficient for small runs or prototypes |
Complement or Competition?
In reality, CNC machining and 3D printing are both competitors and complements, depending on the scenario:
- Competition: For certain plastic or low-volume metal parts, companies may choose either 3D printing or CNC based on cost, speed, and material requirements.
- Complement: Many modern manufacturing workflows combine both: 3D printing prototypes to validate designs, then CNC machining the final parts for production. Hybrid approaches maximize efficiency, reduce waste, and accelerate innovation.
Industry insight: Some aerospace and automotive manufacturers now integrate 3D printing for lightweight components while relying on CNC for structural and high-stress parts—truly getting the best of both worlds.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Project
When deciding between CNC and 3D printing, consider:
- Volume: High-volume production favors CNC; low-volume prototypes favor 3D printing.
- Material and Strength Needs: Metals and high-strength components often require CNC.
- Design Complexity: Intricate shapes may be easier and cheaper with 3D printing.
- Budget and Lead Time: 3D printing reduces prototyping time but can be costlier per unit for production.
Pro tip: Don’t think in terms of “either/or.” Smart manufacturers often blend both to maximize speed, quality, and innovation.
The Bottom Line
CNC machining and 3D printing are not mutually exclusive. Instead, they are two powerful technologies that can enhance each other when used strategically. Understanding the strengths, limitations, and best use cases for each is key to staying competitive in modern manufacturing.
Engagement call: Which technology does your workshop rely on most, and have you tried combining CNC and 3D printing for hybrid projects? Share your experiences in the comments!