When it comes to metalworking, machining has always been at the heart of manufacturing. But today, there’s an ongoing debate: CNC machining vs manual machining. Which one is better? The truth is, both methods have their strengths, and the right choice depends on the job, the budget, and the skill set of the operator. Let’s break down the differences, benefits, and trade-offs in a way that’s easy to understand.
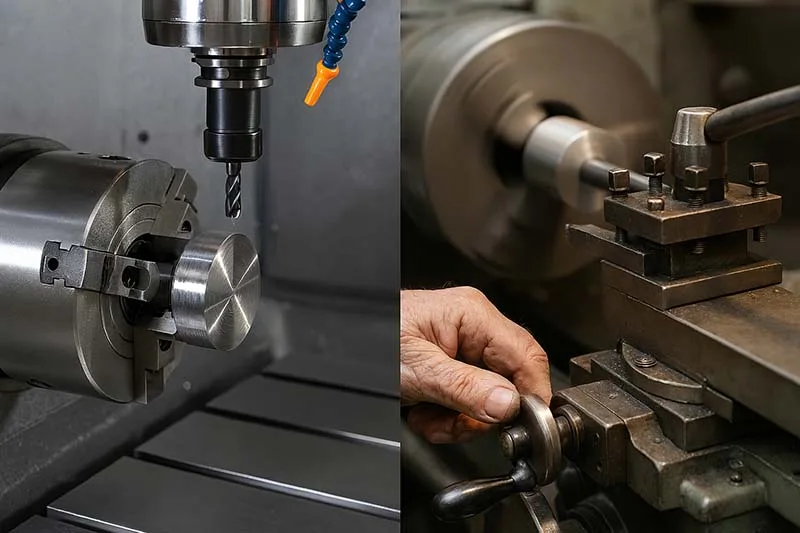
What Is Manual Machining?
Manual machining refers to traditional machine tools like lathes, mills, and grinders operated by hand. The machinist manually adjusts the tool path, feeds, and speeds using wheels, levers, and gauges.
- Pros of manual machining:
- Lower machine cost.
- Ideal for small jobs or one-off parts.
- Allows skilled machinists to improvise and adapt quickly.
- Great for teaching fundamentals of machining.
- Cons of manual machining:
- Slower production speed.
- High dependency on operator skill.
- Difficult to maintain precision on complex parts.
- Not scalable for mass production.
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining uses programmed instructions (G-code and M-code) to control the movements of a machine tool automatically. Once the code is written, the machine executes operations with incredible consistency.
- Pros of CNC machining:
- High accuracy and repeatability.
- Capable of handling complex geometries.
- Faster cycle times for production.
- Easier to scale for mass manufacturing.
- Reduced reliance on manual labor.
- Cons of CNC machining:
- Higher initial investment.
- Requires programming knowledge.
- Maintenance and repairs can be costly.
CNC vs Manual Machining: Head-to-Head
| Factor | CNC Machining | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Setup time | Longer upfront | Shorter |
| Production speed | Much faster | Slower |
| Accuracy & tolerance | Extremely high | Operator-dependent |
| Complex parts | Handles easily | Very difficult |
| Cost efficiency | Great for large runs | Better for small runs |
| Skill requirement | Programming & setup | Hands-on machining skills |
Which One Should You Choose?
- If you’re producing custom prototypes or short runs, manual machining can be faster and cheaper.
- If you’re manufacturing complex or high-volume parts, CNC is the clear winner.
- Many shops actually use both: manual machines for quick, simple jobs, and CNC machines for precision and scale.
A Funny Fact
Did you know that some old-school machinists call CNC machines “button pushers”? The joke is that modern operators just load code and press start—while in reality, programming and setup require just as much expertise.
A Lesser-Known Fact
Manual machining hasn’t disappeared at all. In fact, most CNC operators are trained first on manual machines to understand the fundamentals of cutting, feeds, and tooling before moving on to automation.
Want To Learn More?
- CNC Machining Fundamentals
- CNC Machining Explained: Precision, Process & Possibilities
- CNC Technology: From Punched Tape to Smart Machining
- Types of CNC Machines (Lathe, Mill, Router, Plasma, etc.)
- CNC Programming Languages (G-code, M-code)
- Most Common CNC Programming Errors
- CNC vs Manual Machining: Differences, Pros & Cons Explained
Final Thoughts
The debate of CNC vs manual machining isn’t about which is better overall—it’s about choosing the right tool for the right job. In a perfect world, a modern machine shop has both, using manual machines for quick fixes and CNC machines for precise, scalable production.