Introduction
Manufacturing is a world of moving parts – machines, workers, materials, and endless workflows. Keeping everything efficient and error-free has always been a challenge. Enter process automation, the game-changer that replaces manual, repetitive tasks with smart systems and connected machines.
In this article, we’ll explore how process automation is reshaping modern factories, the benefits it delivers, and what the future holds.
What Is Process Automation in Manufacturing?
Process automation in manufacturing refers to the use of technology, software, and machines to streamline production workflows. Instead of relying solely on human labor, factories now use automated systems to manage tasks such as material handling, assembly, inspection, and data analysis.
Key Tools of Process Automation
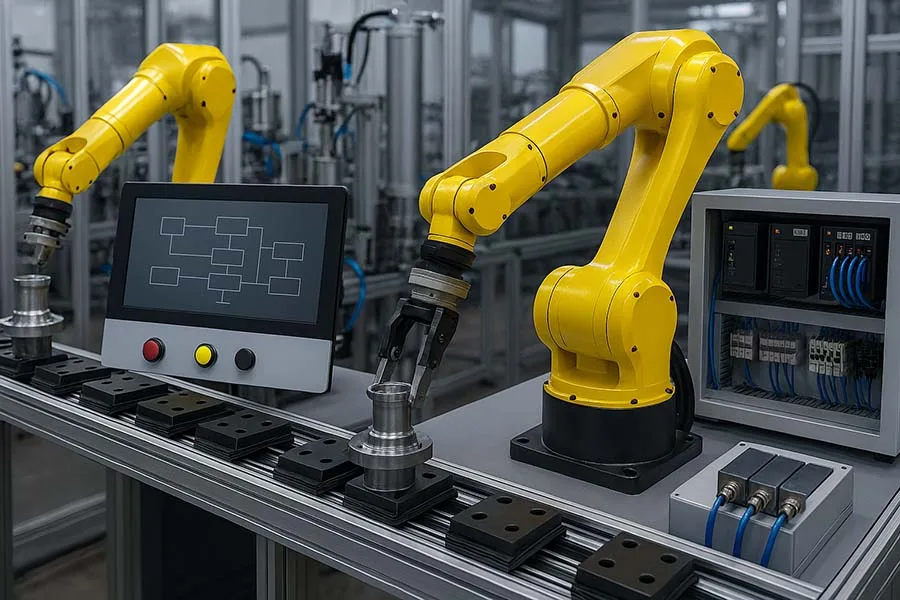
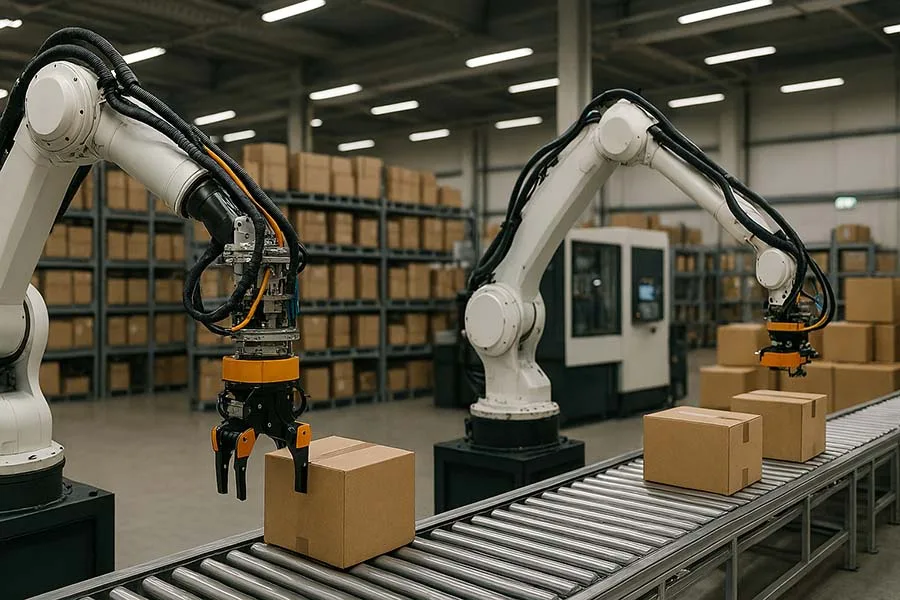
1. Robotics
- Automates repetitive assembly tasks
- Improves accuracy and reduces workplace risks
2. Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
- PLCs, SCADA, and DCS manage complex processes
- Enables real-time monitoring and control
3. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- Tracks and optimizes production in real time
- Connects shop-floor operations with business systems
4. Sensors and IoT Devices
- Provide real-time data on machine performance
- Enable predictive maintenance and energy efficiency
5. AI and Machine Learning
- Optimize scheduling, detect quality issues early
- Drive continuous improvement in processes
Benefits of Process Automation in Manufacturing
- Higher productivity: continuous operations 24/7
- Reduced costs: less waste and fewer errors
- Improved quality: consistent output with minimal variation
- Enhanced safety: machines handle dangerous tasks
- Data-driven decision making: real-time insights guide strategy
Challenges in Implementing Process Automation
- High initial investment in equipment and integration
- Workforce adaptation requiring reskilling and training
- Complex system integration with legacy equipment
- Cybersecurity risks as factories become more connected
The Future of Process Automation
- Hyperconnected factories using 5G and IoT for real-time data flow
- AI-driven self-optimization of production lines
- Sustainable automation reducing energy and material waste
- Collaborative automation where humans and machines work side by side
Funny Fact
One factory tried to automate a cookie packaging line with AI cameras. The problem? The AI couldn’t resist “sampling” cookies – its algorithm flagged too many as defects because they looked “too perfect.” Even robots have trust issues with snacks.
Lesser-Known Fact
The earliest large-scale process automation can be traced back to 1920s Ford Motor Company assembly lines, where mechanical conveyors revolutionized car production. Today’s systems may run on AI, but the roots of automation are almost a century old.
Further Read
- Industrial Automation Solutions – Industrial Tools
- Industrial Automation Systems: The Backbone of Modern Industry – Industrial Tools
- Process Automation in Manufacturing: The Key to Smarter Production – Industrial Tools
- Automation Companies to Watch in 2025 and Beyond – Industrial Tools
- Automation Machines for Industry: Types, Benefits, and Future Trends
- Automated Material Handling Solutions: Benefits, Types & Future Trends
- Automated Control Systems – Industrial Tools
- Industrial Automation Solutions: Transforming Modern Manufacturing
- Warehouse Automation Tools: Boosting Efficiency in Modern Warehouses – Industrial Tools
- Intelligent Automation Technologies: The Future of Industry – Industrial Tools
- Automated Packaging Systems – Industrial Tools
- Automation Case Studies – Industrial Tools
- Automation Trends 2025: What’s Next for Industrial Innovation – Industrial Tools
Conclusion
Process automation is more than a buzzword – it’s the foundation of modern manufacturing. By leveraging robotics, AI, IoT, and control systems, manufacturers can produce faster, safer, and more cost-effectively than ever before.
Do you think factories will ever reach fully automated production with no human intervention? Share your thoughts below – I’d love to hear your take!